|
 |
|
The psychological roots of vaccine hesitancy
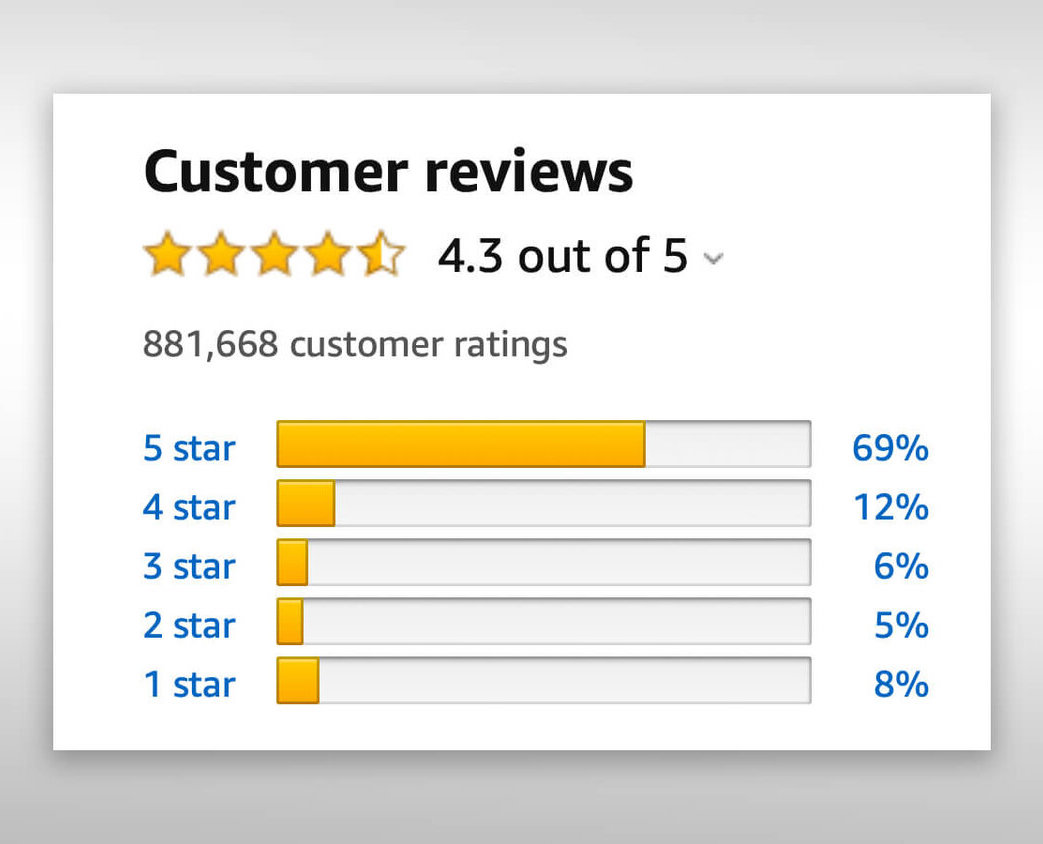
Vaccines have prevented and nearly eliminated several deadly diseases, yet they face skepticism from the public. Vaccination has a favorable risk profile and enormous health benefits, yet there is still widespread skepticism about its safety and efficacy (Edwards & Hackell, 2016). The World Health Organization highlighted vaccine hesitancy as one of the ten focal challenges to global health, partly because of increases in measles outbreaks in countries where the diseases had nearly been eradicated (2019). The vaccination rates needed to maintain herd immunity against a disease varies depending on how contagious it is. For example, measles requires at least a 90 to 95% vaccination rate whereas polio requires about 80 to 85% (Oxford Vaccine Group, 2016).
|